Introduction
In the realms of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), technology has revolutionized the way projects are designed, managed, and executed. Two significant technological advancements in this sector are 3D modelling and Building Information Modeling (BIM). While they may seem similar at first glance, they serve different purposes and offer distinct benefits. This article delves deep into the differences between 3D modelling and BIM modelling, highlighting their unique features, applications, and advantages.
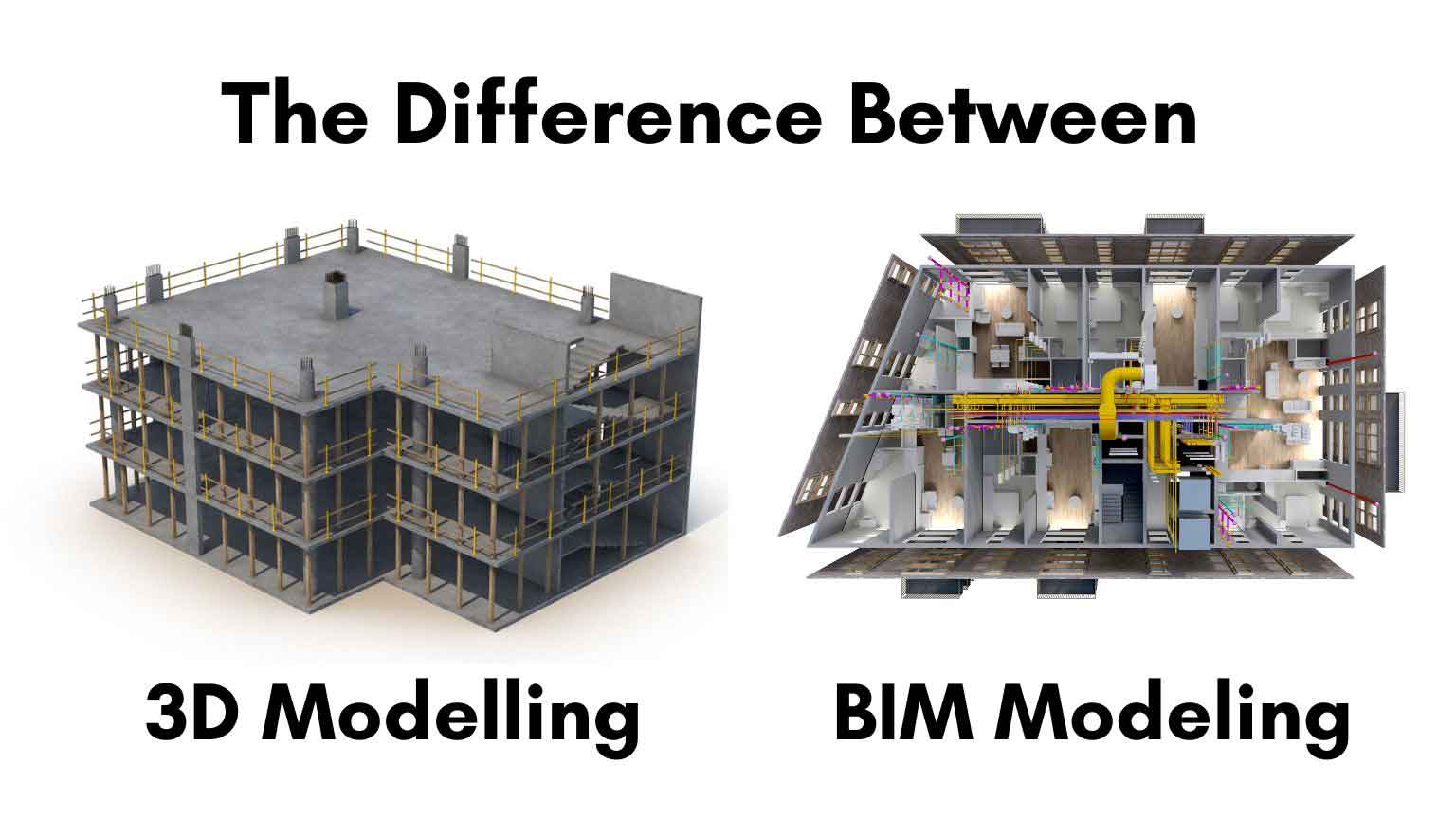
Understanding 3D Modeling
3D modelling is the process of creating a three-dimensional representation of an object or a surface using specialized software. This technique is widely used in various industries, including gaming, film, automotive, and AEC. The primary goal of 3D modelling is to visualize objects in three dimensions, providing a more realistic view than traditional 2D drawings.
Key Features of 3D Modeling
- Visualization: 3D models provide a realistic view of the object, allowing for better visualization and understanding of the design.
- Flexibility: Designers can manipulate the model to view it from different angles and perspectives, making it easier to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
- Detail and Precision: High levels of detail can be incorporated into 3D models, offering precise representations of complex structures and components.
- Animation: 3D models can be animated to demonstrate the functionality and operation of moving parts or systems.
Applications of 3D Modeling
- Architecture and Interior Design: Used to create detailed visualizations of buildings and interior spaces.
- Engineering: Helps in designing and testing mechanical components and systems.
- Entertainment: Essential for creating characters, environments, and special effects in movies and video games.
- Manufacturing: Facilitates the design and prototyping of products.
Understanding BIM Modeling
Building Information Modeling (BIM) goes beyond traditional 3D modelling by incorporating a wealth of information into the digital representation of a building. BIM is an intelligent 3D model-based process that provides architecture, engineering, and construction professionals with the insights and tools to plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure more efficiently.
Key Features of BIM Modeling
- Information-Rich Models: BIM models contain detailed information about building components, including materials, specifications, and performance data.
- Collaboration: BIM enables seamless cooperation between all stakeholders involved in a project, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners.
- Lifecycle Management: BIM supports the entire lifecycle of a building, from initial design through construction, operation, and maintenance.
- Clash Detection: BIM software can automatically detect clashes between different building systems (e.g., HVAC, plumbing), reducing errors and rework.
- Cost Estimation: BIM can be used for accurate cost estimation and budgeting, incorporating both material and labor costs.
Applications of BIM Modeling
- Architecture: Enhances design accuracy and facilitates better decision-making through detailed models and simulations.
- Construction Management: Improves project scheduling, resource management, and construction sequencing.
- Facility Management: Assists in the operation and maintenance of buildings, providing valuable data for repairs, upgrades, and efficiency improvements.
- Infrastructure Projects: Used for complex infrastructure projects like bridges, tunnels, and roads, ensuring better coordination and execution.
Comparing 3D Modeling and BIM Modeling
While both 3D modelling and BIM modelling are essential tools in the AEC industry, they serve different purposes and offer distinct benefits. Here are the main differences between the two:
Purpose and Scope
- 3D Modeling: Primarily focuses on creating detailed visual representations of objects or structures. It is mainly used for visualization, design, and presentation purposes.
- BIM Modeling: Extends beyond visualization to include comprehensive information about every aspect of a building’s lifecycle. BIM models are used for design, construction, and facility management, making them a more holistic approach to building design and management.
Information Content
- 3D Modeling: Contains geometric and spatial information but lacks detailed data about materials, specifications, and performance.
- BIM Modeling: Rich in information, including material properties, specifications, cost estimates, and performance data, enabling better decision-making and project management.
Collaboration and Coordination
- 3D Modeling: Often used in isolation by individual designers or teams with limited collaboration capabilities.
- BIM Modeling: Designed for collaboration, allowing multiple stakeholders to work on the same model simultaneously. BIM facilitates communication and coordination among architects, engineers, contractors, and owners.
Software and Tools
- 3D Modeling: Common software includes AutoCAD, SketchUp, Blender, and Rhino. These tools are primarily focused on creating and editing 3D geometries.
- BIM Modeling: Popular BIM software includes Revit, ArchiCAD, and Navisworks. These tools provide a comprehensive platform for designing, analyzing, and managing building information throughout the project lifecycle.
Lifecycle Management
- 3D Modeling: Limited to the design and visualization phases, with no direct support for construction or facility management.
- BIM Modeling: Supports the entire building lifecycle, from design and construction to operation and maintenance, providing valuable data for all phases of the project.
Advantages of 3D Modeling
- Enhanced Visualization: Provides realistic and detailed views of designs, making it easier to understand and present ideas.
- Design Flexibility: Allows for easy manipulation and modification of models, enabling designers to experiment with different concepts.
- Animation and Simulation: Facilitates the creation of animations and simulations to demonstrate functionality and aesthetics.
Advantages of BIM Modeling
- Improved Collaboration: Enables seamless collaboration among all project stakeholders, reducing errors and improving coordination.
- Comprehensive Data: Provides detailed information about materials, specifications, and performance, supporting better decision-making.
- Lifecycle Management: Supports the entire lifecycle of a building, from design to demolition, ensuring efficient operation and maintenance.
- Cost and Time Savings: Reduces rework and delays through clash detection and accurate cost estimation, leading to significant savings in both time and money.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while 3D modelling and BIM modelling both play crucial roles in the AEC industry, they serve different purposes and offer unique benefits. 3D modelling excels in visualization and design flexibility, making it ideal for creating detailed and realistic representations of objects and structures. On the other hand, BIM modelling provides a comprehensive approach to building design and management, incorporating detailed information and supporting collaboration and lifecycle management.
Ready to bring your ideas to life in stunning 3D? Contact us today to start your project and experience unparalleled quality and creativity in 3D modelling services.